Abstract
Case Report
Large perforating Submandibular Stone-A Case Report
Faaiz Alhamdani*
Published: 09 February, 2018 | Volume 3 - Issue 1 | Pages: 021-024
Salivary stone (sialothiasis) is a calcifying concentration within the ductal system of salivary gland [1]. The majority of salivary calculi occur in the submandibular gland duct because of its length, upward course and the thicker mucus [2].
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001023 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
References
- El Deeb M, Holte N, Gorlin RJ. Submandibular salivary gland sialoliths perforated through the oral floor. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1981; 51: 134-139. Ref.: https://goo.gl/c2Y4pa
- Mitchell DA. Editor. Salivary Glands. Boca Raton: CRC Press. 2015.
- Parkar MI, Vora MM, Bhanushali DH. A Large Sialolith Perforating the Wharton's Duct: Review of Literature and a Case Report. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2012; 11: 477-482. Ref.: https://goo.gl/9L5BGF
- Jadu FM, Jan AM. A meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of managing parotid and submandibular sialoliths using sialendoscopy assisted surgery. Saudi Med J. 2014; 35: 1188-1194. Ref.: https://goo.gl/AP4Upc
- McGurk M, Escudier MP, Brown JE. Modern management of salivary calculi. Br J Surg. 2005; 92: 107-112. Ref.: https://goo.gl/S8Tpxq
- Mehanna H, McQueen A, Robinson M, Paleri V. Salivary gland swellings. BMJ. 2012; 345. https://goo.gl/mZh7NL
- Leite TC, Blei V, Oliveira DPd, Robaina TF, Janini MER, et al. Giant Asymptomatic Sialolithiasis. Int J Oral-Med Sci. 2011; 10: 175-178. Ref.: https://goo.gl/gafHvi
- Patil Ma, Patil SM. An Unusual Large Submandibular Salivary Gland Calculus- A case Report. Indian Journal of Applied Research. 2014; 4: 328-329.
- Siddiqui SJ. Sialolithiasis: an unusually large submandibular salivary stone. Br Dent J. 2002; 193: 89-91. Ref.: https://goo.gl/FKcZ6r
- Babu KL, Jain MK. Giant Submandibular Sialolith: A Case Report and Review of Literature. International Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2011; 2: 154-157.
- Saluja H, Kasat VO, Mahindra U. Giant Sialolith in the Wharton’s duct causing sialo-oral fistula: A case report and review of literature. Journal of Orofacial Sciences. 2016; 4: 137-142. Ref.: https://goo.gl/t8ko8E
- Silva PF, Hage CDA, Pontes FSC, Goncalves FLN, Queiroz APD. Giant Sialoliths: Literature Review and Report of One Case with Mouth Floor Perforation. Journal of Surgical and Clinical Dentistry. 2015; 5: 5-11. https://goo.gl/p2cs9F
- Kraaij S, Karagozoglu KH, Forouzanfar T, Veerman EC, Brand HS. Salivary stones: symptoms, aetiology, biochemical composition and treatment. Br Dent J. 2014; 217: 23. Ref.: https://goo.gl/uSSGYW
- Fowell C, MacBean A. Giant salivary calculi of the submandibular gland. J Surg Case Rep. 2012; 2012: 6. Ref.: https://goo.gl/VBB4GF
- Gupta A, Rattan D, Gupta R. Giant sialoliths of submandibular gland duct: Report of two cases with unusual shape. Contemp Clin Dent. 2013; 4: 78-80. Ref.: https://goo.gl/C5eLJW
- Salerno S, Giordano J, Rusignuolo R, Tona GL, Casto AL. Unusual Sponaneous Salivary Fistula: A retrospective Rview of the Last 12 Years. Acta Medica Mediterranea. 2014; 30: 991-994. Ref.: https://goo.gl/GRXMBi
- Miloro M, editor. Diagnosis and Management of Salivary Gland Disorders. Sl. Louis Missouri: MOSBY. 2008.
- Parkar MI, Vora MM, Bhanushali DH. A Large Sialolith Perforating the Wharton's Duct: Review of Literature and a Case Report. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2011; 11: 477-482. Ref.: https://goo.gl/9L5BGF
Figures:
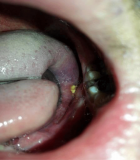
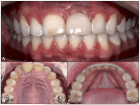
Figure 1
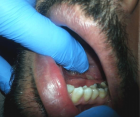
Figure 2
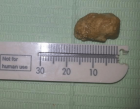
Figure 3
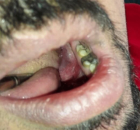
Figure 4
Similar Articles
-
Infection Control Mechanisms Employed by Dental Laboratories to Prevent Infection of their Dental Technicians/TechnologistsKilimo C Sammy*,Simiyu N Benjamin. Infection Control Mechanisms Employed by Dental Laboratories to Prevent Infection of their Dental Technicians/Technologists. . 2016 doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001001; 1: 001-011
-
Evaluation of ImageJ for Relative Bone Density Measurement and Clinical ApplicationManuel Geiger*,Galina Blem,Arwed Ludwig. Evaluation of ImageJ for Relative Bone Density Measurement and Clinical Application . . 2016 doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001002; 1: 012-021
-
Promising Future in the Detection of Oral Cancer by Using Advance Screening TechnologyMohamed Yasser Kharma*,Mohamed Sadek Alalwani,Manal Fouad Amer. Promising Future in the Detection of Oral Cancer by Using Advance Screening Technology . . 2016 doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001003; 1: 022-33
-
Evaluation of Horizontal Lip Position in Adults with Different Skeletal Patterns: A Cephalometric StudyRohit Kulshrestha*,Vinay V Umale,Kamlesh Singh,Aftab Azam,Madhvi Bhardwaj. Evaluation of Horizontal Lip Position in Adults with Different Skeletal Patterns: A Cephalometric Study . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001005; 2: 009-016
-
Normal Value of Skull Base Angle Using the Modified Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technique in Thai PopulationSiriporn Hirunpat*,Nat Wimolsiri,Nuttha Sanghan. Normal Value of Skull Base Angle Using the Modified Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technique in Thai Population . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001006; 2: 017-021
-
Comparative Study of Enophthalmos Treatment with Titanium Mesh Combined with Absorbable Implant vs. Costochondral Graft for Large Orbital Defects in Floor FracturesMalagón Hidalgo*,Héctor Omar,González Magaña,Fernando, Kalach Mussali,Alberto Jaime,Mejía Valero,Sergio Abraham,Vilchis López,Roberto,Araiza Gómez,Edgardo,Kalach Mussali. Comparative Study of Enophthalmos Treatment with Titanium Mesh Combined with Absorbable Implant vs. Costochondral Graft for Large Orbital Defects in Floor Fractures . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001007; 2: 022-29
-
Visualization and Evaluation of Changes after Rapid Maxillary ExpansionIlija Christo Ivanov*,Dagmar Strakova,Tatjana Dostalova,Jan Dupej,Sarka Bejdova,Veronika Ciganova. Visualization and Evaluation of Changes after Rapid Maxillary Expansion . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001008; 2: 030-37
-
Orthodontics Miniscrews to Correct an Anchorage Loss: Case ReportHoub-Dine A*,Zaoui F. Orthodontics Miniscrews to Correct an Anchorage Loss: Case Report. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001009; 2: 038-042
-
External Root Resorption associated with Impacted Third Molars: A Case ReportRenato Marano*,Gabriela Mayrink,Paula Ramos Ballista,Laisa Kinderlly,Stella Araujo. External Root Resorption associated with Impacted Third Molars: A Case Report . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001010; 2: 043-048
-
Clown language training in Dental education: Dental Student’s PerspectiveSiddharth Tevatia*,Richa Dua,Vinita Dahiya,Nikhil Sharma,Rahul Chopra,Vidya Dodwad. Clown language training in Dental education: Dental Student’s Perspective . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001011; 2: 049-056
Recently Viewed
-
Cognitive behavioral therapy treatment for drug addictionAlya Attiah Alghamdi*. Cognitive behavioral therapy treatment for drug addiction. J Addict Ther Res. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jatr.1001025; 7: 005-007
-
Dental Age Estimation using the Cameriere Method in Different Countries: A ReviewDesprika Youhana Sitio*, Ghora March Eka Solehuddin, Grace Sisilia Panjaitan. Dental Age Estimation using the Cameriere Method in Different Countries: A Review. J Forensic Sci Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001062; 8: 035-039
-
Unconventional powder method is a useful technique to determine the latent fingerprint impressionsHarshita Niranjan,Shweta Rai,Kapil Raikwar,Chanchal Kamle,Rakesh Mia*. Unconventional powder method is a useful technique to determine the latent fingerprint impressions. J Forensic Sci Res. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001035; 6: 045-048
-
Difference between conventional and modern methods for examination of fingerprintsAmbati Ramesh Babu*. Difference between conventional and modern methods for examination of fingerprints. J Forensic Sci Res. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001025; 5: 037-040
-
Gilbert’s Syndrome Revealed by Hepatotoxicity of ImatinibImen Ben Amor*,Imen Frikha,Moez Medhaffer,Moez Elloumi. Gilbert’s Syndrome Revealed by Hepatotoxicity of Imatinib. Ann Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.acgh.1001049; 9: 001-003
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."