Abstract
Research Article
Enamel demineralization with resin modified gic and conventional composite resin - a comparative in vivo study
Gautam G*, Shashikala Kumari V, Garima Garg and Vikram Shetty
Published: 31 July, 2017 | Volume 2 - Issue 3 | Pages: 069-079
Background & Objectives: Fluoride releasing bonding agents can help the orthodontist to minimize enamel demineralization independent of patient cooperation. This in vivo study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy of resin modified glass ionomer cement (RMGIC) on reducing enamel demineralization around orthodontic brackets and confirm the superior caries-preventive effect of RMGIC by assessing the mutans streptococci (S. mutans) in plaque samples in vitro.
Methods: 60 subjects (aged 14-20 years) scheduled to have premolar extractions as part of the orthodontic treatment plan were selected and randomly divided into 2 groups of 30 each (group 1: the brackets were bonded on the teeth using light cure composite resin and group 2: the brackets were bonded using RMGIC). Plaque scores (modification of plaque index by Silness and Loe) were recorded and plaque samples were collected before bonding, one week and one month after bonding. S.mutans colonies were recorded from the plaque samples inoculated on MSB agar plates, incubated under 95% N2 and 5% CO2 for 48 hours at 370C in a CO2 jar. After 1 month, the right maxillary and mandibular first premolars were debonded, extracted and depth of enamel demineralization area was estimated using polarized light microscope.
Results: After statistical analysis, a significantly higher mean depth of demineralized lesions was noticed in group 1 as compared to group 2. A significant difference between occlusal and gingival depth was seen only in group 2, thus illustrating a wedge effect. In group 1, a statistically significant increase in the mean colony forming units (CFU) of S.mutans has been noticed at different time intervals whereas in group2, a significant increase was observed only at 1month. Unlike at 1 month, a statistically significant difference in mean CFU between group 1 and group 2 has been observed at 1 week (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Enamel lesions adjacent to the bracket base on teeth bonded with the RMGIC were smaller than those on teeth bonded with a composite resin. The high “burst effect” of fluoride release for the first few days of RMGIC after bonding is confirmed by statistically significant reduction in CFU counts of S. mutans in plaque.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001014 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
RMGIC; White spot lesion; Enamel demineralization; Mutans streptococci
References
- O'Reilly MM, Featherstone JDB. Demineralization and remineralization around orthodontic appliances: an in vivo study.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1987; 92: 33-40. Ref.: https://goo.gl/bicr2b
- Sundararaj D, Venkatachalapathy S, Tandon A, Pereira A. Critical evaluation of incidence and prevalence of white spot lesions during fixed orthodontic appliance treatment: A meta-analysis. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2015; 5: 433-439. Ref.: https://goo.gl/XZa6rN
- Tantbirojn D, Douglas WH, Versluis A. Inhibitive effect of a resin-modified glass ionomer cement on remote enamel artificial caries. Caries Res. 1997; 31: 275-280. Ref.: https://goo.gl/bDFZRS
- Pascotto RC, Navarro MF, Capelozza Filho L, Cury JA. In vivo effect of a resin-modified glass ionomer cement on enamel demineralization around orthodontic brackets. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004; 125: 36-41. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ZRkcsf
- Lundström F, Krasse B. Streptococcus mutans and lactobacilli frequency in orthodontic patients; the effect of chlorhexidine treatments. Eur J Orthod. 1987; 9: 109-116. Ref.: https://goo.gl/EyKNCa
- Marsh PD. Dental plaque as a biofilm: the significance of pH in health and caries. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2009; 30: 76-78. Ref.: https://goo.gl/QH38Wf
- Wright AB, Lee RT, Lynch E, Young KA. Clinical and microbiologic evaluation of a resin modified glass ionomer cement for orthodontic bonding. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1996; 110: 469-475. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ayjyN7
- Wheeler AW, Foley TF, Mamandras A. Comparison of fluoride release protocols for in-vitro testing of 3 orthodontic adhesives. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002; 121: 301-309. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ff35KV
- Hammersfahr P. Developments in resionomer systems in glass-ionomers. In: Hunt PR, editor. Glass ionomers: the next generation. Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Glass-Ionomers. Philadelphia, PA: International Symposia in Dentistry. 1994; 47-55.
- Tarn LE, Chan GP, Yim D. In vitro caries inhibition effects by conventional and resinmodified glass-ionomer restorations. Oper Dent. 1997; 22: 4-14. Ref.: https://goo.gl/iy1SMb
- Vorhies BA, Donly KJ, Staley RN, Wefel JS. Enamel demineralization adjacent to orthodontic brackets bonded with hybrid glass ionomer cements: An in vitro study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1998; 114: 668-674. Ref.: https://goo.gl/TzqnVz
- Matalon S, Slutzky H, Weiss EI. Antibacterial properties of 4 orthodontic cements. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2005; 127: 56-63. Ref.: https://goo.gl/87eb84
- Schmit JL, Staley RN, Wefel JS, Kanellis M, Jakobsen JR, et al. Effect of fluoride varnish on demineralization adjacent to brackets bonded with RMGI cement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002; 122: 125-134. Ref.: https://goo.gl/QGSsqr
- Gorton J, Featherstone JD. In vivo inhibition of demineralization around orthodontic brackets. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003; 123: 10-14. Ref.: https://goo.gl/tq4nDo
- Rosenbloom RG, Tinanoff N. Salivary Streptococcus mutans levels in patients before, during, and after orthodontic treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1991; 100: 35-37. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Mzm1pU
- Amezquita AN, Lucia MT, Jaramillo A, Betancourth M, Enrique JB. Changes in the subgingival microbiota and periodontal parameters before and 3 months after bracket placement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006; 130: 275. Ref.: https://goo.gl/EKAETb
- Newbrun E. Cariology 3rd ed. Quintessence Publishing Co. Inc, Chicago, Illinois. 1989; 13-61.
- Silverman E, Cohen M, Demke RS, Silverman M. A new light-cured glass ionomer cement that bonds brackets to teeth without etching in the presence of saliva. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1995; 108: 231-236. Ref.: https://goo.gl/8MrU4W
- Gutiérrez de Annan S, de Valladares RER, de Cardenas ILB. Mitis salivarius-bacitracin 10% sacarose agar for oral streptococci and Streptococcus mutans counts. Acta Odontol Latinoam. 1997; 10: 47-53. Ref.: https://goo.gl/smygjr
- Mattingly JA, Sauer GJ, Yancey JM, Arnold RR. Enhancement of Streptococcus mutans Colonization by Direct Bonded Orthodontic Appliances. J Dent Res. 1983; 62: 1209-1211. Ref.: https://goo.gl/bjgxLk
- Yengopal V, Mickenautsch S. Caries-preventive effect of resin-modified glass-ionomer cement (RM-GIC) versus composite resin: a quantitative systematic review. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2011; 12: 5-14. Ref.: https://goo.gl/93rPqg
- Brantley AW, Eliades T. editors: Orthodontic materials- scientific and clinical aspects, Stuttgart, Germany. 2001.
- Friedl KH, Schmalz G, Hiller KA, Shams M. Resin-modified glass ionomer cements: fluoride release and influence on Streptococcus mutans growth. Eur J Oral Sci. 1997; 105: 81-85. Ref.: https://goo.gl/iaE1BJ
- Fishman SA, Tinanoff N. The effect of acid and fluoride release on the antimicrobial properties of four glass ionomer cements. Pediatr Dent. 1994; 16: 368-370. Ref.: https://goo.gl/C3CmCZ
- Ahn SJ, Lim BS, Lee YK, Nahm DS. Quantitative Determination of Adhesion Patterns of Cariogenic Streptococci to Various Orthodontic Adhesives. Angle Orthod. 2006; 76: 869-875. Ref.: https://goo.gl/HBQo3s
- McGhee JR, Michalek SM. Immunobiology of dental caries: microbial aspects and local immunity. Annu Rev MicrobioI. 1981; 35: 595-638 Ref.: https://goo.gl/o3wDXc
Figures:
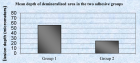
Figure 1
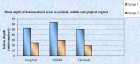
Figure 2
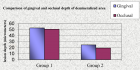
Figure 3

Figure 4

Figure 5
Similar Articles
-
Enamel demineralization with resin modified gic and conventional composite resin - a comparative in vivo studyGautam G*,Shashikala Kumari V,Garima Garg,Vikram Shetty. Enamel demineralization with resin modified gic and conventional composite resin - a comparative in vivo study . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001014; 2: 069-079
Recently Viewed
-
A Comparative Study of Metoprolol and Amlodipine on Mortality, Disability and Complication in Acute StrokeJayantee Kalita*,Dhiraj Kumar,Nagendra B Gutti,Sandeep K Gupta,Anadi Mishra,Vivek Singh. A Comparative Study of Metoprolol and Amlodipine on Mortality, Disability and Complication in Acute Stroke. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001108; 9: 039-045
-
Development of qualitative GC MS method for simultaneous identification of PM-CCM a modified illicit drugs preparation and its modern-day application in drug-facilitated crimesBhagat Singh*,Satish R Nailkar,Chetansen A Bhadkambekar,Suneel Prajapati,Sukhminder Kaur. Development of qualitative GC MS method for simultaneous identification of PM-CCM a modified illicit drugs preparation and its modern-day application in drug-facilitated crimes. J Forensic Sci Res. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001043; 7: 004-010
-
A Gateway to Metal Resistance: Bacterial Response to Heavy Metal Toxicity in the Biological EnvironmentLoai Aljerf*,Nuha AlMasri. A Gateway to Metal Resistance: Bacterial Response to Heavy Metal Toxicity in the Biological Environment. Ann Adv Chem. 2018: doi: 10.29328/journal.aac.1001012; 2: 032-044
-
Obesity in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease as a Separate Clinical PhenotypeDaria A Prokonich*, Tatiana V Saprina, Ekaterina B Bukreeva. Obesity in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease as a Separate Clinical Phenotype. J Pulmonol Respir Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001060; 8: 053-055
-
Current Practices for Severe Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Associated COPD and EmphysemaMJ Nicholson*, M Seigo. Current Practices for Severe Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Associated COPD and Emphysema. J Pulmonol Respir Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001058; 8: 044-047
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."